
Current Version: 1.36 (14th March 2024)
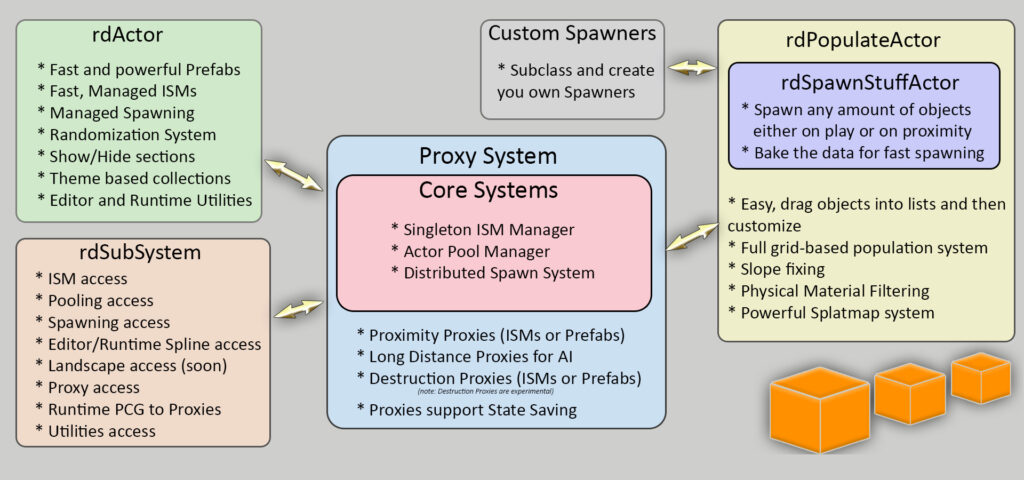
rdInst is an optimized C++ plugin that can speed up your levels by huge amounts.
You can use it to take care of your ISMs – by converting StaticMesh Actors and harvesting instances from volumes in your level (each volume has it’s own set of draw calls) you can significantly reduce the amount of draw calls.
That’s only the first level of optimization though – using the rdInst Spawning systems, you can spawn your objects when they reach a specified proximity – this can be used with or without world partition streaming – and you can spawn more spawning systems, giving you the ability to create extremely complex levels in the most optimal way.
Rather than spawning things such as AI and vehicles straight into the level (or anything with collision for that matter) you have the option to spawn them as ISMs – which swap to the AI/vehicle etc when they are closer to the player – Proxies.
It also takes care of all your Spawned Actors, Child Components,Actor Pools, Randomization and Selective Hiding/Showing of these objects, Proxies and Spline Editing.
Using rdInst you can optimize your whole level, both FPS and VRAM.
rdInst also contains Proximity Spawners and Proxies – enabling large amounts of spawned objects and AI.
The plugin can be used in two ways:
- As an Editor plugin, providing optimized editing and fast randomization, baking out the results into fast blueprint only actors using either just static meshes or utilizing any method of instancing – or even baked into static meshes (great for Nanite). rdBPtools is completely compatible with rdInst and uses its optimizations when you use its Base Blueprints.
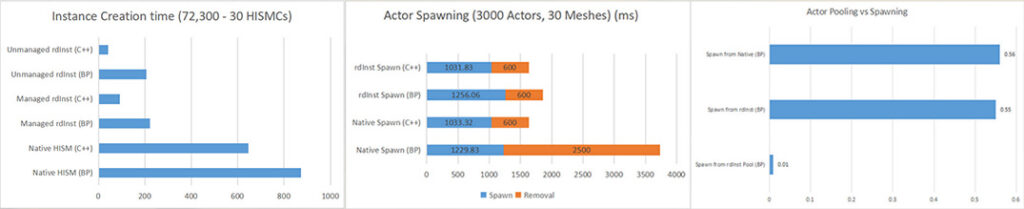
- As a runtime plugin, packaged along with your project. Providing it’s instancing and spawning routines, and its optimizations for use in real-time – such as randomizing a room to a specific seed before moving it into place. In fact, it is this part that provides the best optimization. You can have many objects in your rooms, each with their own random settings – using rdInst, you don’t even see a drop in framerate when randomizing. Blueprint routines to randomize are somewhat slower – especially when actors rely on other actors to be visible.
Just use the included rdActor as your base actor, or directly call library functions.
Instances are managed according to their owning actor, during Editing this allows fast editing of large amounts of meshes – during runtime this allows fast Showing/Hiding of actors and even sub-folders of meshes for each actor.
Non-managed functions are available too – these give raw access to the HeirachialInstanceStaticMesh Components used to create the instances.
It’s as simple as calling the “rdAddInstance” node in your Blueprints, specifying the Static Mesh and a Transform. Removing them is as simple as using the “rdRemoveInstances” – it only removes instances used by your current blueprint.
Some of the main features of rdInst are:
- Very Easy to create Instances of Static Meshes
- All Instances are managed, and looked after behind the scenes
- Access to the actual Instance generators for raw power
- Complete Scalable Procedural Population system supporting SplatMaps, slope fixing, material filtering etc.
- Spawn new Actors in a Managed way from Construction Scripts
- Proximity Spawners of various types
- Actor Pools for extremely fast Actor Spawning
- Component Pools for extremely fast Component generation
- Distributed Transactions – spawn actors and instances over multiple frames to reduce the load
- Swap Instances or Prefabs in to Proxy Actors when close – add things like collision cylinders to close trees
- Have Hierarchies of Actors/Instances, show and hide whenever, from the Editor or at Runtime
- Assimilate child instances into their parents
- Apply Randomization of Child Actors Transform and visibility with a sophisticated Randomization system
- Use “Themes”, control the sets of visible Actors/Instances by a Theme
- Convert any Instance to a ChildComponent or a Level Actor at Runtime
- Find the Instances Parent from HitScans
- Fast Instance Transformations without rebuilding
- Easy way to set Instance Render Settings for Static Meshes
- Easy way to set Per-Instance Custom Floats for each Instances materials
- Speeds up rendering while in the Editor – smoother editing large amounts of objects
- Subsystem to handle instancing and pooling from any actor
- Editor and Runtime Editing, Splitting, Joining and Populating of Splines
- Convert PCG volumes into fast Proxy scanning data at runtime to swap in actors in proximity
Randomization parameters can be used to add variety to the instances transform (and visibility). The Randomization system is inherited from owner actors, so it’s easy to make systems where you control all your Randomization from one Random Seed.
Swap Instances into Actors in proximity – a great way to save both FPS and VRAM:

At a longer distance, Long-Distance Proxies swap to AI and back:
Even run-time baking of other volumes such as PCG volumes with Proxies etc added as it bakes.
If you’re using rdInst as a runtime plugin, it gets included with your Packaged Build (be sure to disable the plugin when packaging if you’re not using it). The source code is well documented, and written in a way that should require very minimum maintenance in the future, very easy for anyone with VS to build to a new UE version.
This plugin is completely compatible with rdBPtools, rdBuildBuddy and rdBeacons and can significantly improve rendering times by using with these tools. It is for sale on the Unreal Marketplace.